How Does AI Humanizer Work
AI text models have been around since the early 2010s, but they exploded in popularity roughly a few years ago, and in 2025, they’re still taking over everything. From blog posts and ad copies to eBooks, research papers, and even product descriptions - AI-generated text is literally everywhere.
People got smarter, too. Readers, editors, and even casual users can now tell when something sounds too AI. Flat tone, perfect grammar, same rhythm in every sentence - it’s easy to spot once you’ve seen enough of it. That’s where AI humanizers come in. Their job is to disguise or, more accurately, refine AI-generated writing so it feels genuinely human, both to real readers and to AI detectors.
And now, the market is packed with these AI-to-human text converters. But here’s the big question everyone keeps asking: Do they actually work? Let’s break it down.
Does AI Humanizer Really Work?
Yes, they actually do. The whole point of an AI humanizer is to take a piece of text that clearly sounds like it was written by a machine and make it read like something created by a person. The idea is simple: fix the rhythm, smooth out the grammar, and bring back a natural flow that doesn’t scream “AI.”
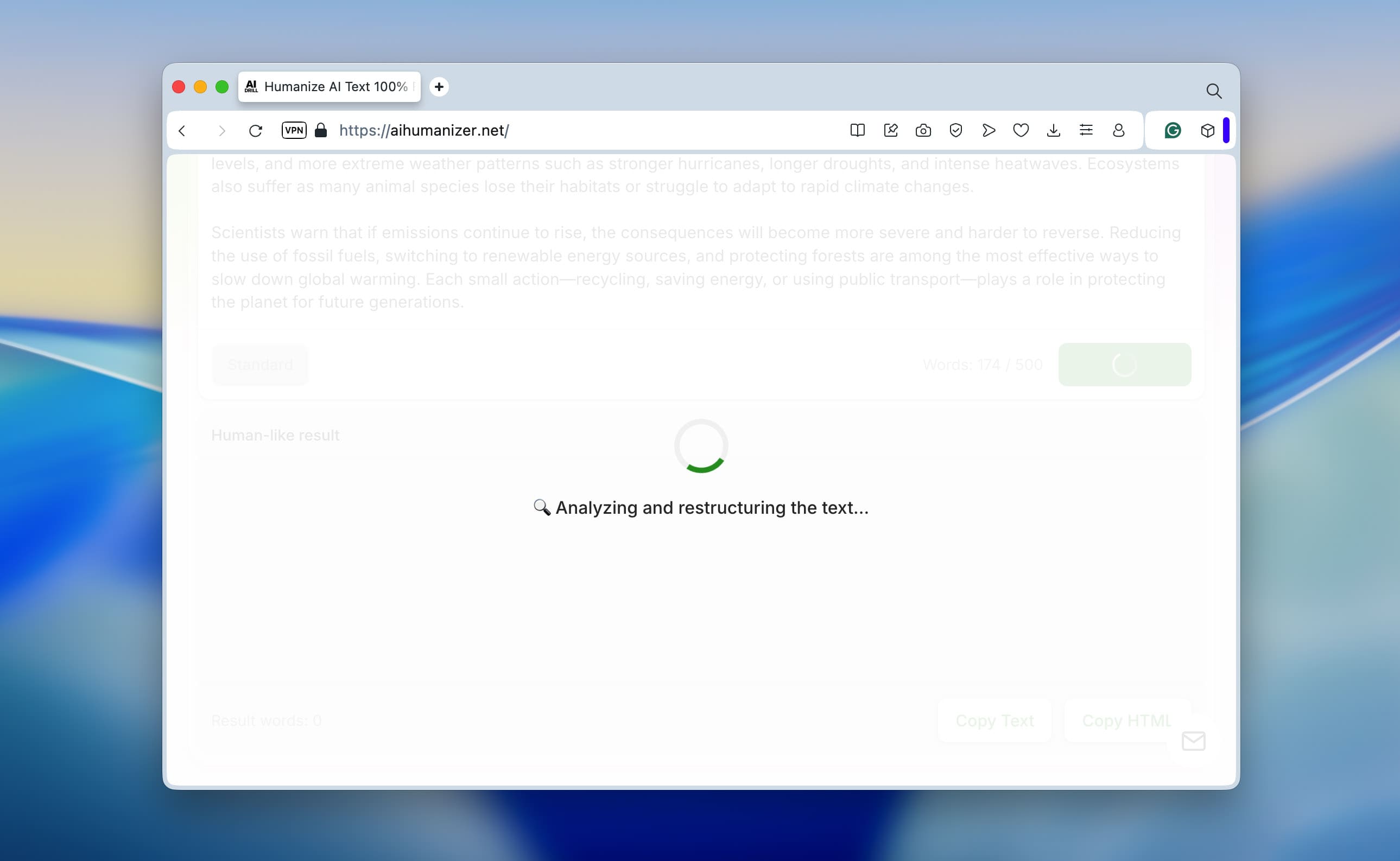
To show how this works in practice, we ran a quick test. We generated a short paragraph in ChatGPT-5, the kind of text you can spot as AI from a mile away. It had all the usual signs: perfectly structured sentences, identical length, polished grammar, and that signature double dash (—) that large language models love to use. And yes, even the dash shape gives it away, real people typically use the shorter en dash (–), while AI tends to overuse em dashes.
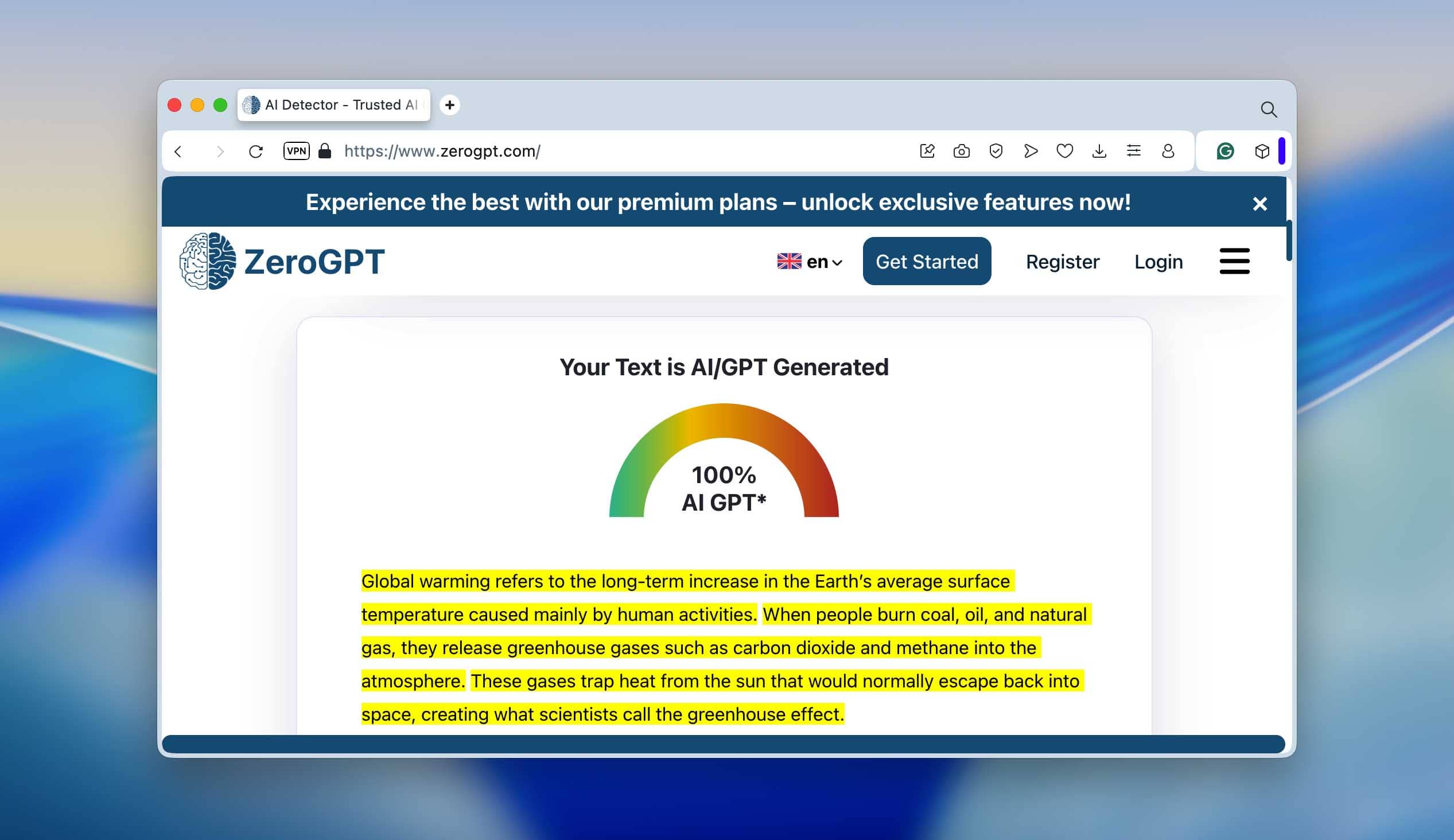
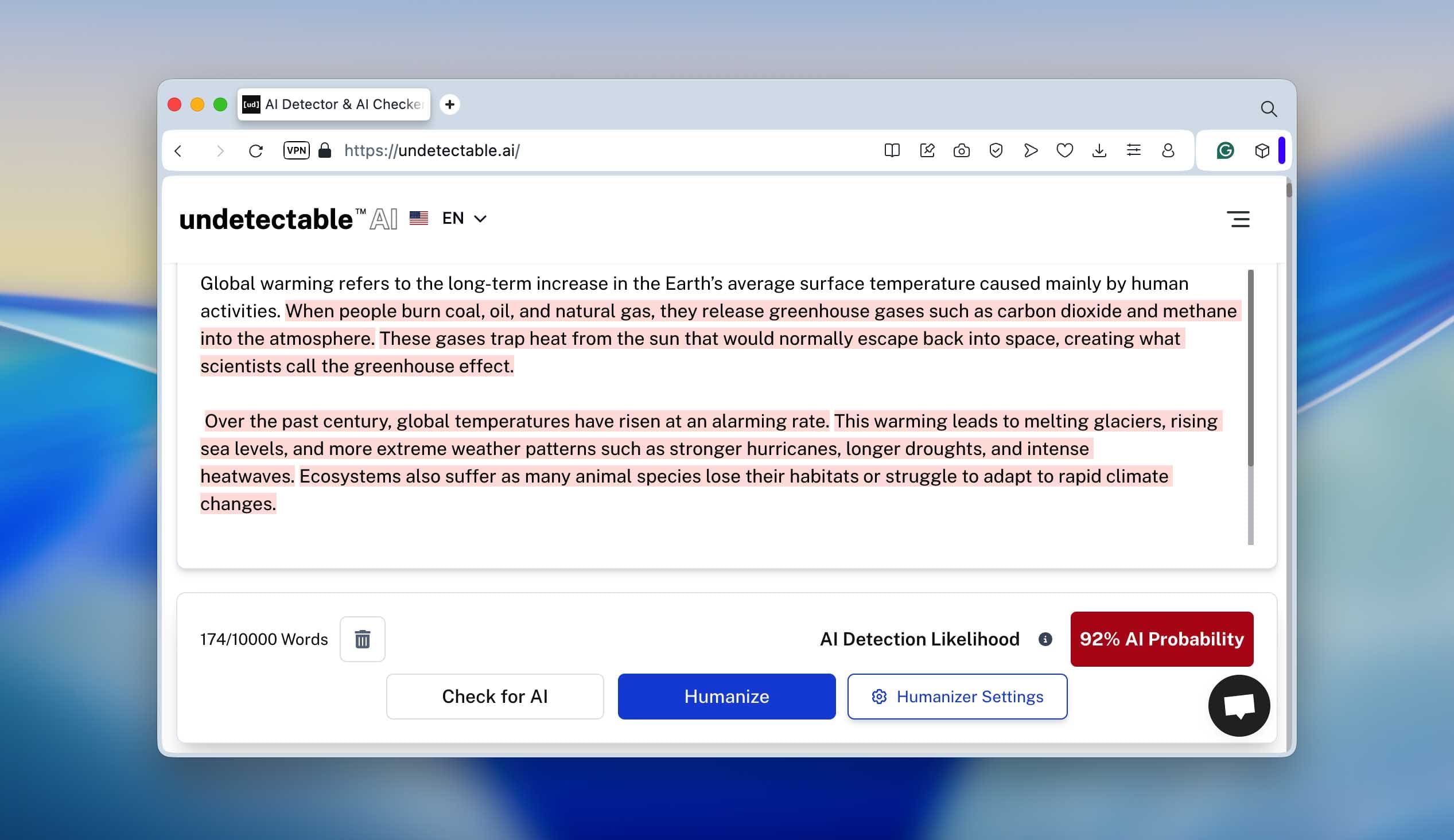
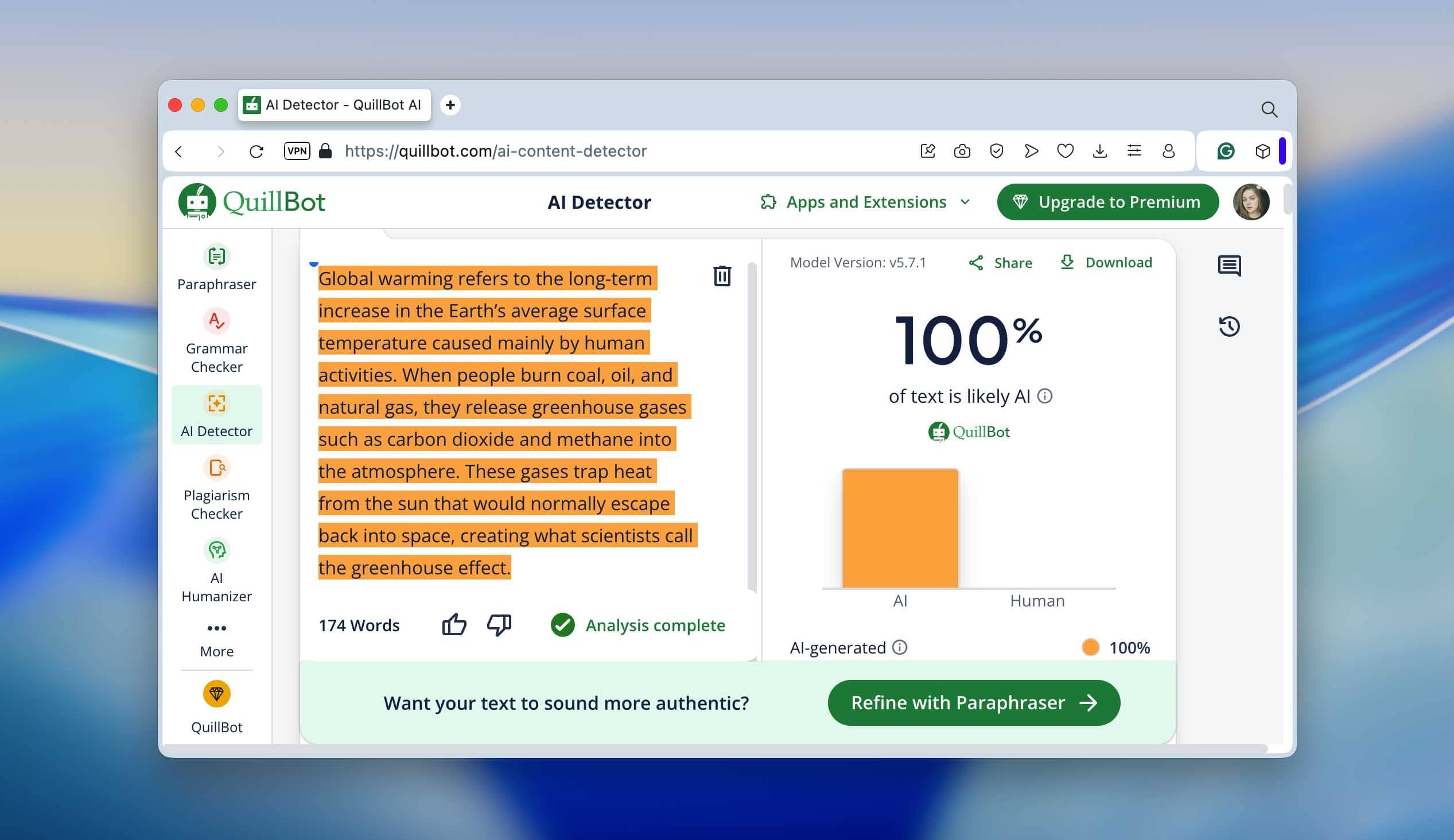
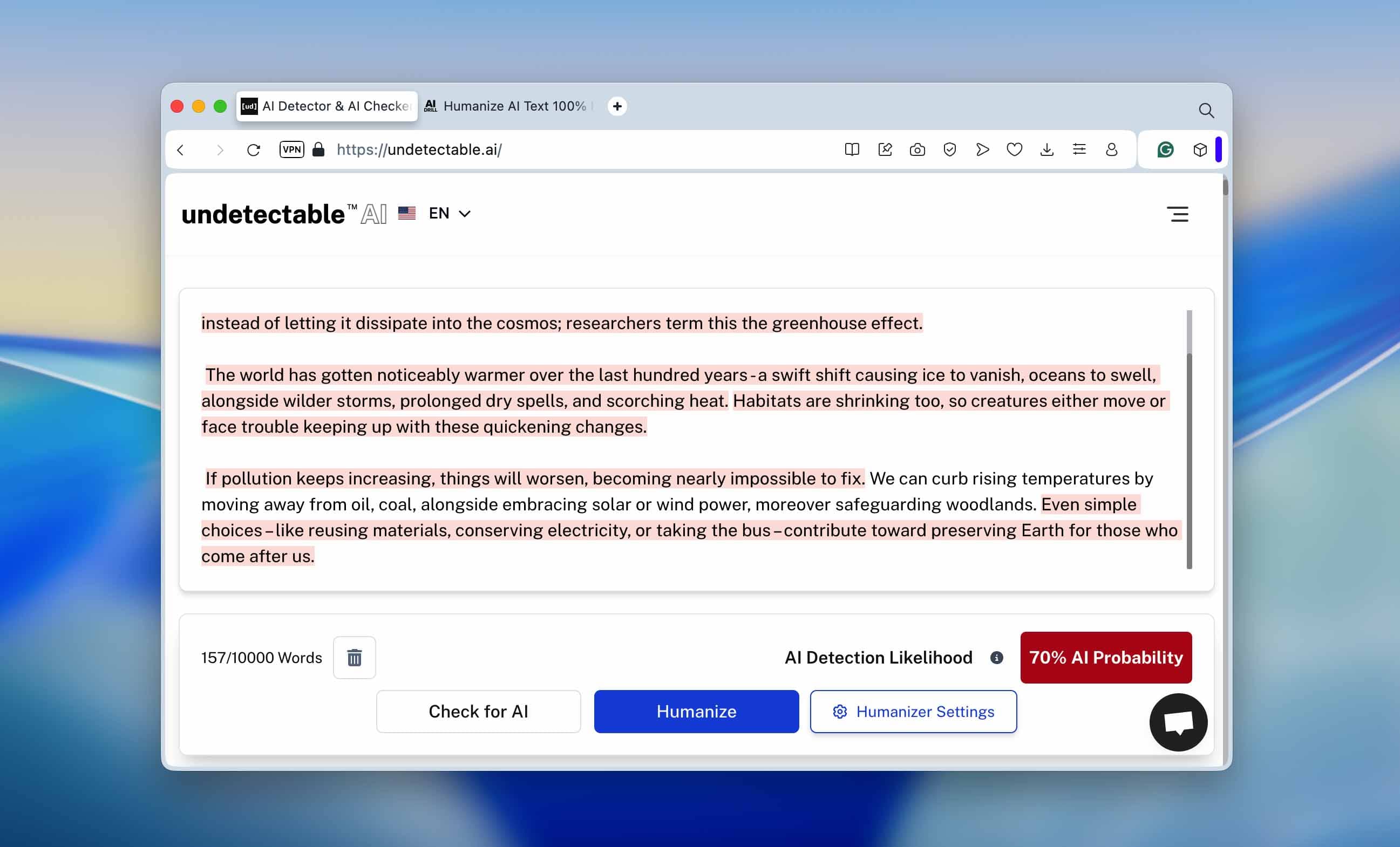
We then tested this raw version in three well-known AI detectors - ZeroGPT, Undetectable.ai, and QuillBot’s AI Checker. The results were almost identical: every one of them confidently marked the text as 100% AI-generated. You can see the detection scores in the screenshots below - they’re pretty clear.
-
ZeroGPT

-
Undetectable.ai

-
QuillBot’s AI Checker

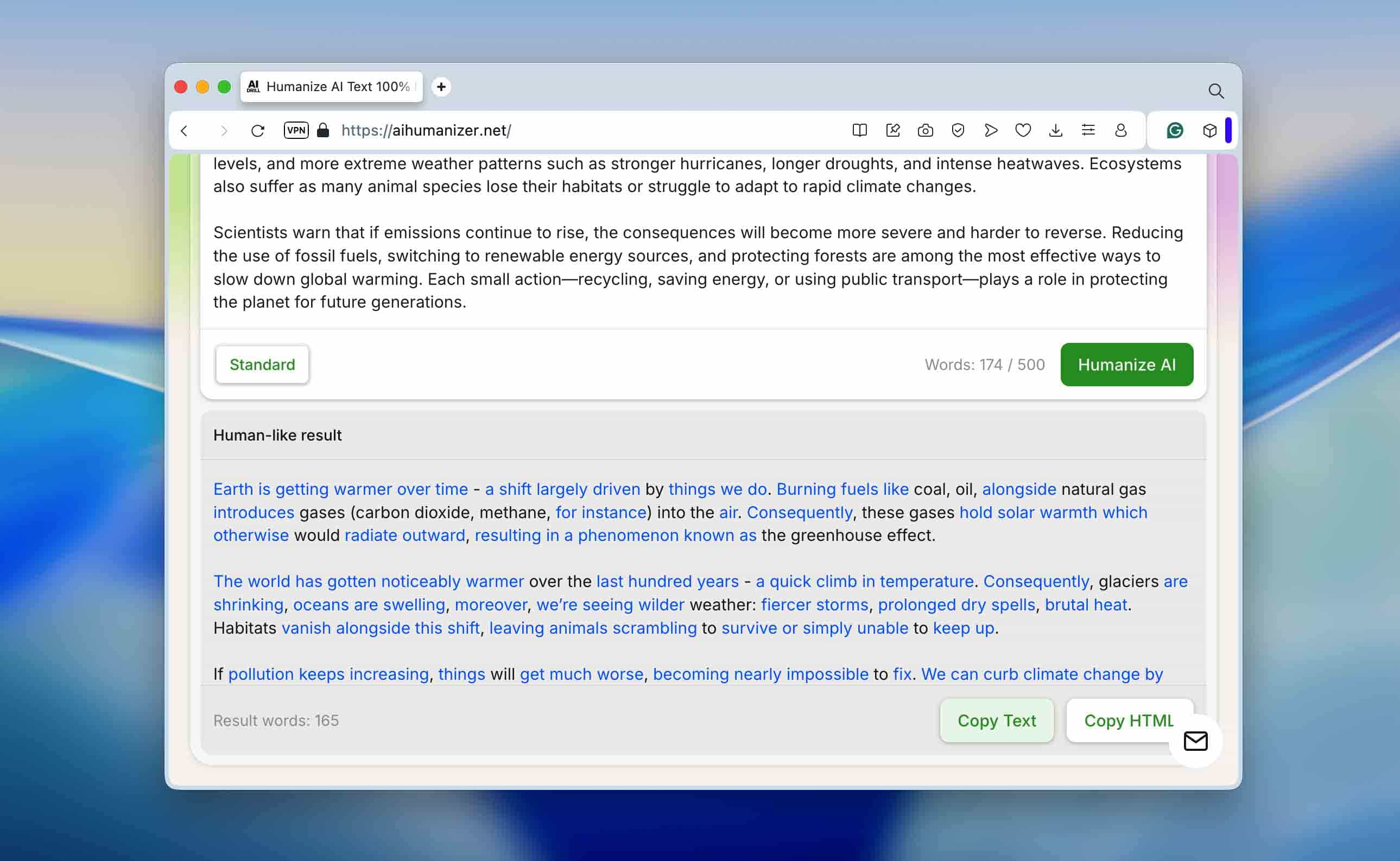
After that, we ran the same paragraph through a text humanization tool to see how much the tone and structure could improve. The output looked much more natural. Sentence length varied, transitions sounded more human, and the text didn’t feel overly “balanced.” Most importantly, grammar stayed clean while the AI detection rate dropped noticeably across all the tools we used.
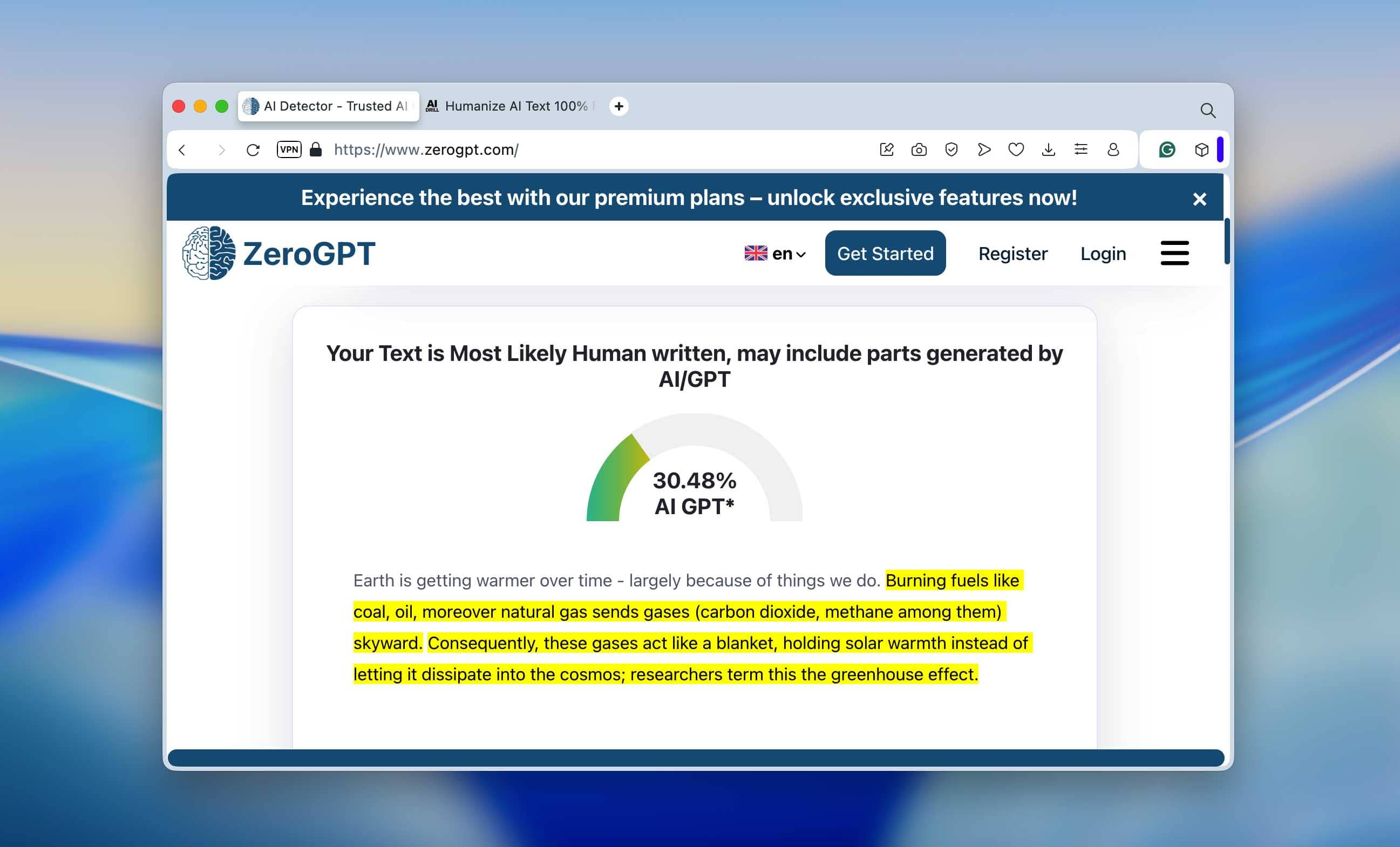
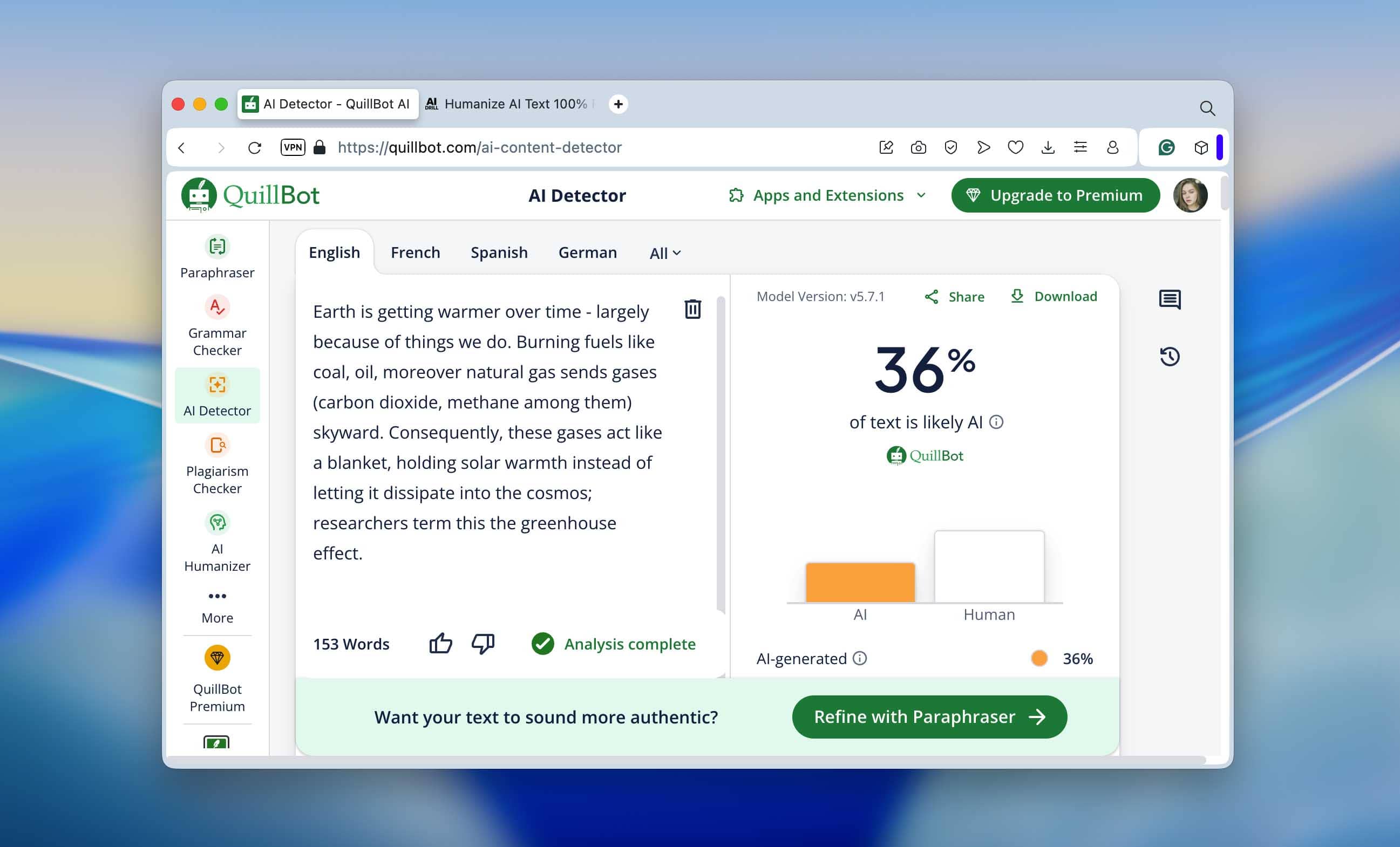
We ran the humanized version through the same detectors again. This time, the results dropped significantly: ZeroGPT and QuillBot both showed around 30% AI, while Undetectable.ai still marked about 70%. Why such a difference? Most likely, each detector uses its own scoring logic (different thresholds, token-probability analysis, and pattern weightings). For instance, some tools rely heavily on perplexity and entropy, while others focus on sentence rhythm or word-choice variance.
-
ZeroGPT

-
Undetectable.ai

-
QuillBot’s AI Checker

Still, that’s only an educated guess. The exact algorithms behind these detectors remain undisclosed, only their developers truly know how they work.
Now, let’s make one thing clear. No AI humanizer can guarantee a perfect 0% AI score. That’s not because they fail (it’s because the detectors themselves aren’t perfect either). Many humanizers work differently, and their accuracy often depends on training data, token probabilities, and even the model version.
If you scroll through Reddit, you’ll see tons of discussions where real users complain that AI detectors marked their own writing as “AI.” That’s because each detector often uses its own proprietary datasets and evaluation criteria. In fact, this behaviour was characterised in the study where the authors introduced the RAID benchmark to test the performance of various AI-text detectors.
In that study, authors evaluated both commercial and open-source detectors by feeding them sequences of tokens and asking each detector to output a scalar score Ѕ. To decide whether a text is machine-generated, the rule is: S ≥ δ(threshold) ⇒ machine-generated prediction
They set the threshold so that the false positive rate (human text marked as AI) is about 5% for each model. Then they reported detector accuracy on the machine-generated part of the dataset.
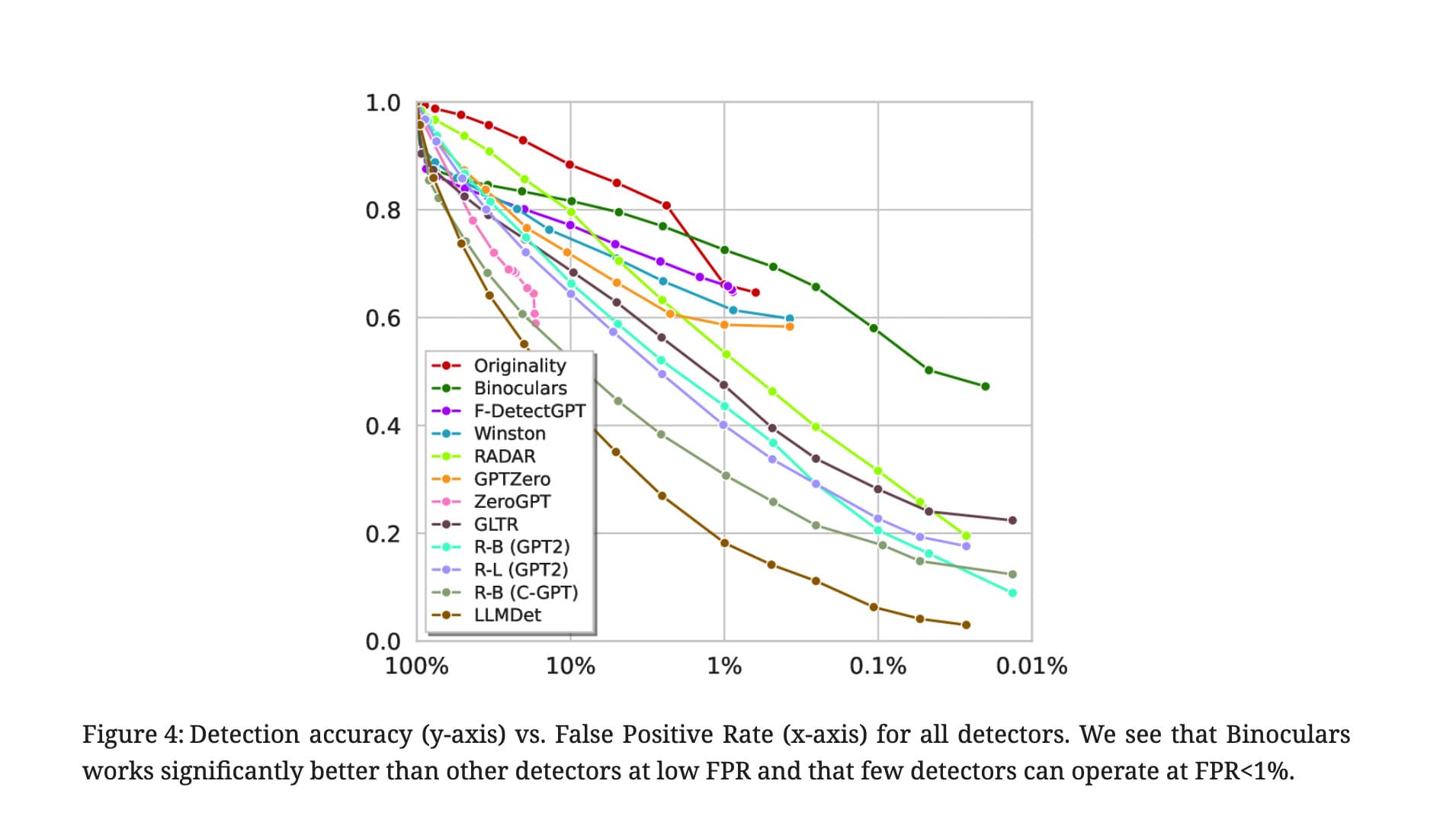
The authors also produced heat maps showing how detectors like RoBERTa, GPTZero, and RADAR perform across different LLMs and domains. The maps clearly show bias: detectors perform much better on models and domains they were trained or tuned on, but drop off when they face unseen generators or domains. In short, detection scores vary not only by how “AI-like” the text is, but also by which model generated it and what domain the text comes from.

So, the goal isn’t to fool every checker. It’s to find the balance, to make your content sound human, stay readable, and pass through detection systems without losing meaning or quality.
What Types of AI Humanizers Exist?
As mentioned earlier, not all AI humanizers work the same way. The exact process depends on the algorithm built into each tool. Some rely on old-school rule sets, while others use advanced language models or combine several approaches at once. In general, we can group AI humanizers into three main categories based on how they process and rewrite text:
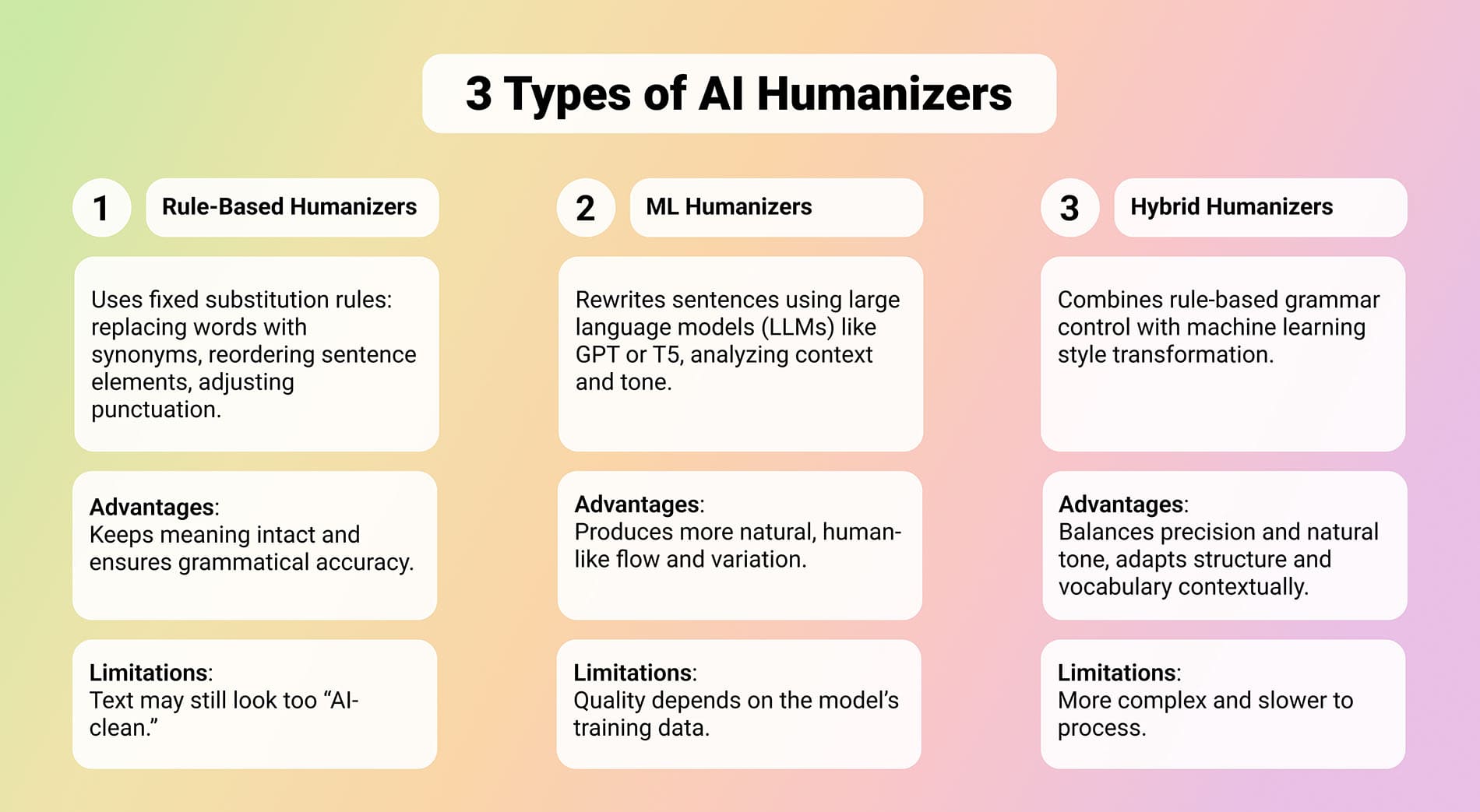
- Rule-based humanizers are the most traditional type. They follow fixed patterns and substitution rules (replacing words with synonyms, reordering basic sentence elements, or tweaking punctuation). Their strength is stability: they rarely distort meaning because they keep the original sentence structure intact. But that’s also their biggest limitation, since the structure doesn’t really change, the text may still look too “AI-clean” to advanced detectors.
- Machine-learning-driven humanizers use large language models (LLMs) such as GPT-based or T5-based systems to rewrite entire sentences, not just swap words. They analyze the context, tone, and flow of the text, then generate a new version that preserves meaning but feels more human. They’re much more flexible but slightly less predictable - results can vary depending on the model’s training data.
- Hybrid humanizers (NLP + ML) combine both methods: rule-based processing for grammatical safety and machine learning for style transformation. The hybrid approach allows for context-aware synonym replacement, tone adaptation, and sentence restructuring - all while running internal checks to ensure the text keeps its original meaning.
Today, the most common tools are those based on large language models, they handle both meaning and tone with far greater flexibility. Meanwhile, rule-based systems still serve a purpose but are now used mostly for proofreading rather than real text transformation. A great example is Grammarly. It does an impressive job of spotting grammar mistakes, fixing punctuation, and polishing sentence structure. Still, it’s not really built to humanize writing - its synonym choices and phrasing often feel a bit stiff or overly formal, more like a rule-based correction tool than a natural writer.
How Does AI Humanizer Work?
Now that we’ve seen that AI humanizers really work, it’s time to look at how they actually do it. The answer depends on which side you’re viewing it from.
How AI Humanizers Work for Users
For regular users, it’s simple. Let’s take Clever AI Humanizer as an example. To use it (or any other humanizer), you just:
-
Go to the Clever AI Humanizer website and locate the text box on the main page.

-
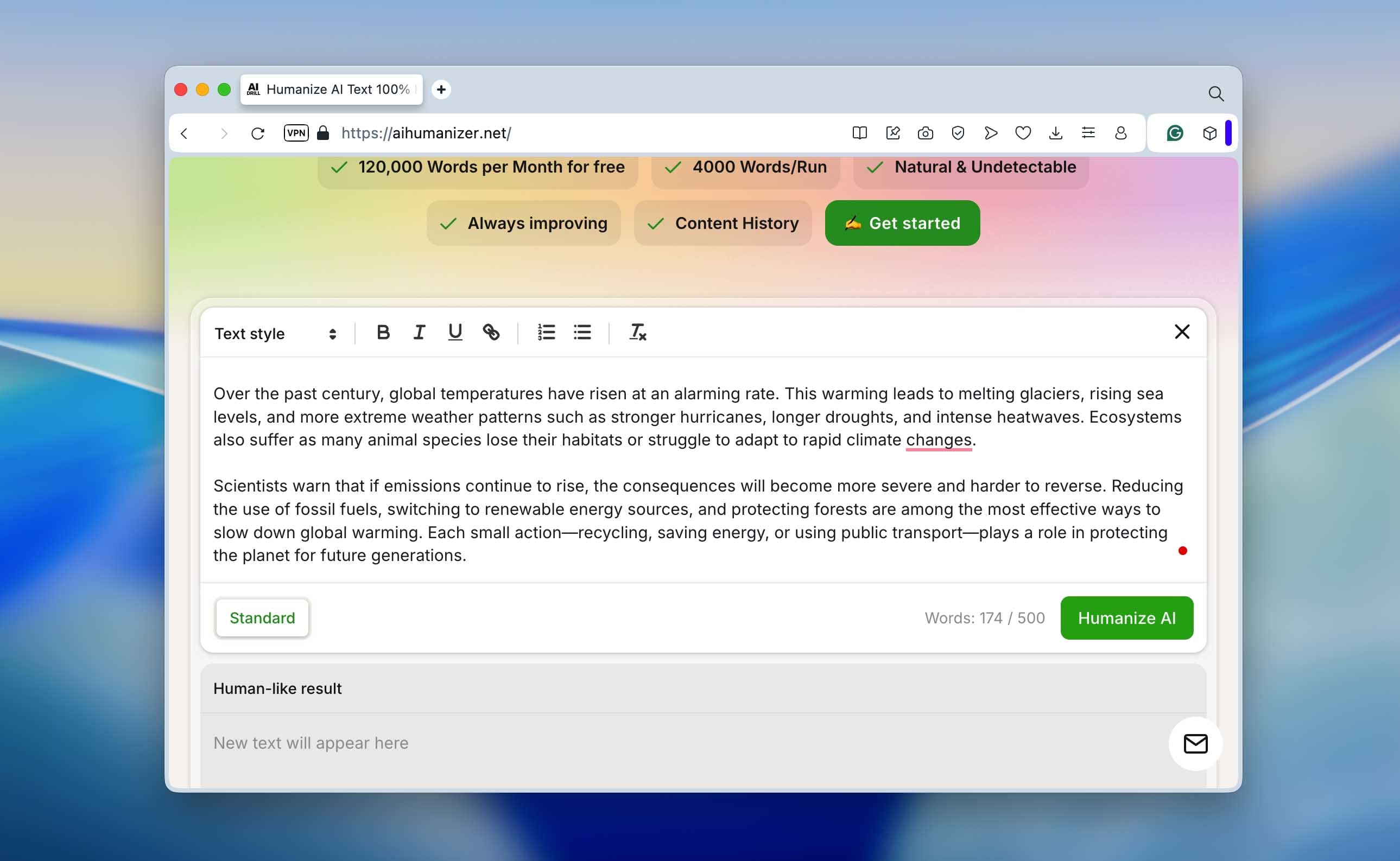
Paste your AI-generated content into that box and double-check that it meets the minimum word count. Most platforms won’t run if the text is too short, Clever AI Humanizer, for instance, requires at least 30 words. When you’re ready, press the “Humanize AI” button.

-
Give it a few seconds to process.

-
Once the tool finishes, you’ll get a refreshed version of your text: sentences flow with different lengths, punctuation feels more natural, and repetitive words are replaced with varied synonyms that sound right in context. After that, you’re free to do whatever you need - run it through AI detectors again, fine-tune the details, or publish it straight away.

How AI Humanizers Work Behind the Scenes
Behind the scenes, things are a lot more complex. Different humanizers use different techniques, but most of them rely on the same core logic - rewriting text to break predictable AI patterns while keeping meaning intact. Here’s what usually happens inside:
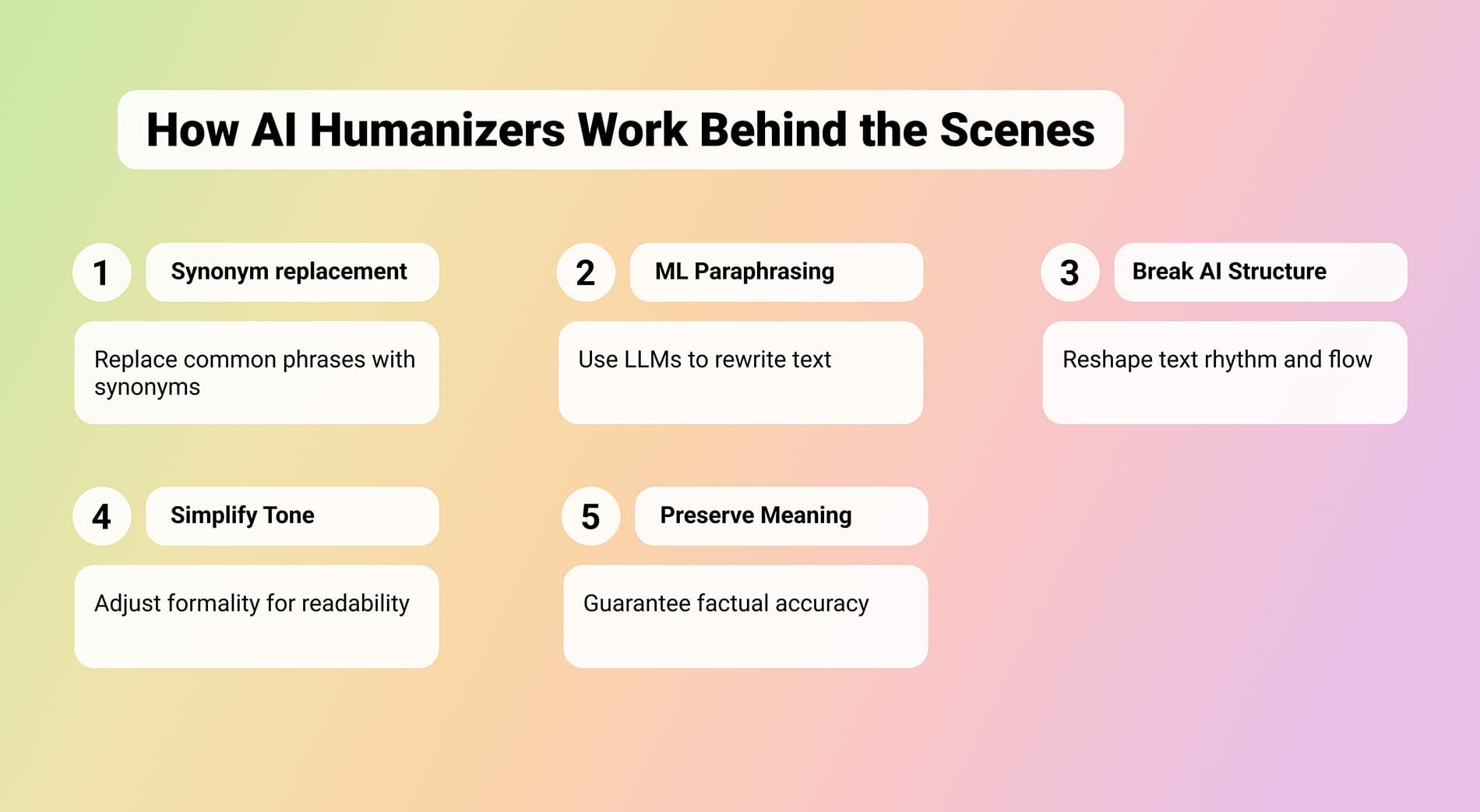
- Synonym replacement. This is the simplest layer. The tool identifies repetitive or common AI phrases and replaces them with contextually suitable synonyms. The structure of the sentence stays mostly the same, but the surface wording changes. But modern tools like Clever AI Humanizer don’t stop there.
- Machine-learning paraphrasing. Advanced humanizers use language models (LLMs) such as GPT-based or T5-based systems to rewrite the text. These models analyze entire sentences or even paragraphs to understand the meaning before restructuring them. They can reorder sentences for better flow, merge or split phrases naturally, and swap predictable phrasing for more human-like alternatives. The goal behind all of this is to increase randomness and burstiness (the small imperfections that make writing sound human) without losing clarity.
- Breaking AI writing structure. Humanizers also reshape how text “feels.” AI tends to produce long, balanced sentences that read like Wikipedia entries. Humanizers break that rhythm by splitting, combining, or reordering ideas to mimic real human thought.
- Simplifying or balancing the tone. Some tools simplify overly formal AI text into something closer to a human reading level. That doesn’t mean dumbing it down, it just makes it easier to read. Others focus on balancing tone (less robotic precision, more flow, a few natural imperfections).
- Preserving meaning. A good humanizer never changes facts. It checks that the rewritten text still means the same thing.
Of course, not every humanizer works exactly like this. Some rely purely on surface-level rewriting and synonym swaps; others combine rule-based logic with machine learning models for deeper restructuring.
We understand it might be interesting to see how this process looks in mathematical form, with real formulas and measurable steps. Most AI humanizers you’ll find online are commercial tools, and it’s reasonable that their developers prefer to keep their algorithms private since that’s what makes their products valuable.
However, to understand the general principle of how a humanizer works, we can look at one of the transparent research projects available - a paraphrase generation model called DIPPER. This model can rewrite entire paragraphs while considering their context and controlling both lexical diversity (word changes) and content reordering (sentence structure), which coincides with the action of ML humanizers.
The model takes a sentence or paragraph and rewrites it while adjusting two measurable properties: lexical diversity and order diversity. Lexical diversity reflects how much the rewritten text differs in word choice compared to its original version. It can be expressed as: L = normalized unigram token overlap(pi...pj, shuffle(pi′...pj′))
Order diversity instead tracks how much the model rearranges the original token order. That is measured using Kendall’s tau correlation coefficient: O = Kendall − τ(token_map(pi...pj, shuffle(pi′...pj′)))
Both values, L and О, typically range from 0 to 100. Higher numbers tell the paraphraser to be more creative: break the familiar rhythm of AI writing, vary sentence shape, and disguise predictable generation patterns. The model is guided by these two numbers, which are injected directly into its input. In simplified form, the prompt passed to the system looks like this: < lex = L, order = O > ⊕ pi...pi−1 ⊕ < p > shuffle(pi′...pj′) < p > ⊕ pj+1...pN
Instead of merely swapping individual words with synonyms, the tool produces a newly rewritten piece that preserves the meaning but disrupts the patterns that detectors expect to see. In its graphical form, this algorithm can be represented as follows:

Another algorithmic strategy involves retrieval-driven rewriting, where a humanizer compares your text against a large library of existing outputs, ideally ones that are confidently human. First, the system converts the text into an embedding vector: v = fret(y)
It then searches for the closest matches from previously collected writings, each also represented as vectors in the same space. The similarity is measured like this: score = maxi v × vi ‖v ‖‖vi ‖
If the score is too similar to what an AI model has produced before, the system rewrites the phrasing until the distance between vectors grows (nudging the style closer to natural examples and farther from a recognizable “AI signature”).
Can an AI Humanizer Be Detected?
Yes, and no at the same time. We’d love to say that Clever AI Humanizer is a fully undetectable AI humanizer, but in reality, detection results depend heavily on the quality of the original text.
If the author barely spent time on the prompt and simply told an AI model, “write me something about this,” the output will almost always look 100% machine-written. In that case, a humanizer, no matter how good, can only reduce the “AI score” so far. It will still help, but traces of automated writing usually remain. That’s exactly what happened in our earlier test - even after humanizing, one of the detectors still showed a noticeable percentage of AI.
However, if you take time to craft a thoughtful prompt, add structure, specify the tone, and include stylistic details, the base text itself will already look more authentic. Instead of starting from a 100% AI-detected draft, you might begin at around 50%. From there, tools like Clever AI Humanizer have a much easier job. They only need to adjust the remaining machine-like parts, and that’s where an undetectable AI humanizer works best.